Q.1 Phenol, when it first reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid and then with concentrated nitric acid, gives
(a) 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene
(b) o-nitrophenol
(c) p-nitrophenol
Sulfonation
The reaction of phenol with concentrated sulfuric acid is thermodynamically controlled. At 25°C, the ortho product predominates while at 100°C, the para product is the major product.
Nitration
Q.2 α-D-(+)-glucose and β-D-(+)-glucose are
(a) conformers
(b) epimers
(c) anomers
Q.3 HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to give
(a) CH3CHO and CH3Br
(b) BrCH2CHO and CH3OH
(c) BrCH2 – CH2 – OCH3

(a) 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene
(b) o-nitrophenol
(c) p-nitrophenol
(d) nitrobenzene
Explanation:-
Sulfonation
The reaction of phenol with concentrated sulfuric acid is thermodynamically controlled. At 25°C, the ortho product predominates while at 100°C, the para product is the major product.
Notice that at both 25° and 100°, initially an equilibrium is established. However, at the higher temperature, the equilibrium is destroyed and the more thermodynamically stable product is produced exclusively.
Nitration
Phenol, when treated with dilute nitric acid at room temperature, forms ortho‐ and para‐nitrophenol
Answer (b) o-nitrophenol
Q.2 α-D-(+)-glucose and β-D-(+)-glucose are
(a) conformers
(b) epimers
(c) anomers
(d) enantiomers
Explanation:-
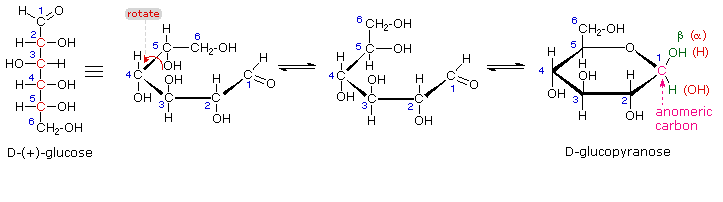
Anomers are stereoisomers of cyclic sugars that differ in configuration only at the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon.
Glucose is both an aldehyde at C-1 and an alcohol at C-5. These two groups can react with each other to form a cyclic hemiacetal (glucopyranose).
 www2.chemistry.msu.edu
www2.chemistry.msu.edu
In the hemiacetal, C-1 has become chiral. It can have the OH group either "down" or "up". These two isomers are anomers, and C-1 (the original carbonyl carbon) is the anomeric carbon.
Answer (c) anomers Glucose is both an aldehyde at C-1 and an alcohol at C-5. These two groups can react with each other to form a cyclic hemiacetal (glucopyranose).
 www2.chemistry.msu.edu
www2.chemistry.msu.eduIn the hemiacetal, C-1 has become chiral. It can have the OH group either "down" or "up". These two isomers are anomers, and C-1 (the original carbonyl carbon) is the anomeric carbon.
Q.3 HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to give
(a) CH3CHO and CH3Br
(b) BrCH2CHO and CH3OH
(c) BrCH2 – CH2 – OCH3
(d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3
Explanation:-
Methyl vinyl ether is a very reactive gas. It is hydrolysed rapidly by dilute acids at room temperature to give methanol and aldehyde.
However, under anhydrous conditions at room temperature, it undergoes many addition reactions at the double bond.
Methyl vinyl ether is a very reactive gas. It is hydrolysed rapidly by dilute acids at room temperature to give methanol and aldehyde.
However, under anhydrous conditions at room temperature, it undergoes many addition reactions at the double bond.
Answer (d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3


No comments:
Post a Comment